Ayurveda is a traditional system of medicine that has its roots in ancient India. The word “Ayurveda” is derived from the Sanskrit words “Ayur,” meaning life, and “Veda,” meaning knowledge or science. Ayurveda, therefore, translates to “the science of life” or “the knowledge of life.”
Principles and components of Ayurveda include:
1. Holistic Approach: Ayurveda views health as a state of balance among the body, mind, and spirit. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of these aspects and recognizes the importance of addressing all three to achieve overall well-being.
2. Doshas: Ayurveda categorizes individuals based on three fundamental energies or doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. Each person has a unique combination of these doshas, which influence their physical and mental characteristics, as well as their susceptibility to imbalances and diseases.
• Vata: Associated with air and ether, governs movement.
• Pitta: Associated with fire and water, governs transformation and metabolism.
• Kapha: Associated with earth and water, governs structure and stability.
3. Prakriti and Vikriti: Prakriti refers to an individual’s natural constitution or doshic makeup, while Vikriti refers to the current state of imbalance or disease. Ayurveda aims to identify and address imbalances to restore the natural state of health.
4. Diet and Nutrition: Ayurveda places significant emphasis on the role of diet in maintaining health. Different doshic types are believed to benefit from specific dietary choices, and Ayurvedic dietary guidelines aim to balance the doshas.
5. Herbal Medicine: Ayurveda utilizes a wide range of herbs and botanicals for therapeutic purposes. Herbal remedies are often prescribed to address specific imbalances or health concerns.
6. Ayurvedic Diagnosis: Ayurvedic practitioners assess an individual’s doshic constitution, current imbalances, and overall health through methods such as pulse diagnosis, examination of the tongue, observation, and questioning about lifestyle and symptoms.
7. Seasonal Lifestyle Practices: Ayurveda recognizes the influence of seasons on health and recommends seasonal adjustments in diet, lifestyle, and daily routines to maintain balance.
8. Mind-Body Connection: Ayurveda recognizes the influence of mental and emotional factors on physical health. Practices such as meditation and mindfulness are considered important for maintaining mental and emotional balance.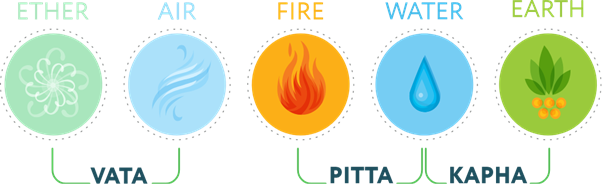
Understanding the imbalance of your unique body is the basis for treatment.
 Shirodhara is a traditional Ayurvedic therapy that involves gently pouring a continuous stream of warm oil or other liquids onto the forehead (the “third eye” area) for a specific duration. The term “Shirodhara” is derived from the Sanskrit words “shiro” (head) and “dhara” (flow). This therapeutic procedure has been used for centuries as part of Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine originating in India.
Shirodhara is a traditional Ayurvedic therapy that involves gently pouring a continuous stream of warm oil or other liquids onto the forehead (the “third eye” area) for a specific duration. The term “Shirodhara” is derived from the Sanskrit words “shiro” (head) and “dhara” (flow). This therapeutic procedure has been used for centuries as part of Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine originating in India.
Benefits of Shirodhara:
1. Detoxification: The warm oil used in Shirodhara is often infused with herbal extracts, and the therapy is thought to assist in the detoxification process by promoting the elimination of toxins.
2. Relaxation and Stress Reduction: Shirodhara is renowned for its ability to induce a deep state of relaxation. The gentle flow of warm liquid has a calming effect on the nervous system, helping to reduce stress and promote mental tranquility.
3. Balancing Doshas: According to Ayurveda, individuals have unique combinations of the three doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha—that influence their physical and mental characteristics. Shirodhara is believed to help balance these doshas and restore harmony to the body and mind.
4. Improved Sleep: Shirodhara is often recommended for individuals experiencing sleep disturbances or insomnia. The calming effect of the therapy can promote better sleep patterns.
5. Scalp and Hair Health: The continuous flow of oil nourishes the scalp and hair, potentially improving hair texture and promoting overall scalp health.
6. Third Eye Activation: The point on the forehead where the liquid is directed is considered a vital energy point in Ayurveda, often referred to as the “third eye” or “ajna chakra.” This area is associated with intuition and higher consciousness.
7. Enhanced Cognitive Function: Some proponents of Shirodhara believe that the therapy can improve mental clarity, concentration, and memory by calming the mind and supporting overall brain function.
8. Spiritual Connection: In addition to its physical and mental benefits, Shirodhara is sometimes regarded as a spiritual practice. The experience of the continuous flow of liquid is believed to foster a sense of connection with higher consciousness.
9. Management of Certain Conditions: Shirodhara is used as a complementary therapy for various conditions, including anxiety, depression, headaches, migraines, and certain neurological disorders.
Panchakarma is a comprehensive detoxification and rejuvenation program in Ayurveda, the traditional system of medicine from India. The term “Panchakarma” translates to “five actions” in Sanskrit, referring to the five therapeutic procedures that form the core of this cleansing and healing process. The primary goal of Panchakarma is to eliminate accumulated toxins (ama) from the body and restore balance to the doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha), the fundamental principles governing the body’s functioning. Panchakarma is performed individually for each person, taking into account their unique constitution and particular disorder, it necessitates careful observation and supervision.
The five main procedures of Panchakarma are:
1. Vamana (Therapeutic Vomiting): This helps eliminate Kapha-related disorders.
2. Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Aimed at eliminating excess Pitta dosha and toxins from the gastrointestinal tract and liver. It helps in conditions related to liver disorders, skin issues, and digestive problems.
3. Basti (Enema Therapy): Basti is used to address Vata dosha imbalances.
4. Nasya (Nasal Administration): Nasya is primarily employed to clear excess Kapha from the head and respiratory passages.
5. Raktamokshana (Bloodletting): Raktamokshana is performed to purify the blood and remove excess Pitta-related toxins. Methods, including venipuncture, leech therapy, or other blood-cleansing techniques, are used to eliminate impurities from the blood.
Benefits of Panchakarma:
1. Detoxification: Panchakarma helps eliminate accumulated toxins from the body.
2. Balancing Doshas: It helps restore balance to the three doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha.
3. Enhanced Digestion: Panchakarma supports improved digestion and metabolism.
4. Stress Reduction: The therapies promote relaxation and mental well-being.
5. Improved Immunity: It enhances the body’s natural defenses and immunity.
6. Rejuvenation: Panchakarma contributes to overall rejuvenation and vitality.
